Las Vegas Air Force Station
|
Las Vegas Air Force Station (1956-1969) - A Cold War Air Force Radar Station first established in 1956 near Las Vegas, Clark County, Nevada. Named Las Vegas Air Force Station after the location. Initially assigned a Permanent ID of SM-163, later a Sage ID of Z-163. Abandoned by the Air Force in 1969 now Angel Peak FAA Radar Site with an FAA ID of QAS. HistoryEstablished in 1956 and became operational on 1 April 1956 as Las Vegas Air Force Station manned by the 865th AC&W Squadron. The station initially had both a Ground-Control Intercept (GCI) and an early warning mission. The early warning mission involved tracking and identifying all aircraft entering their airspace while the GCI mission involved guiding Air Force interceptors to any identified enemy aircraft. Controllers at the station vectored fighter aircraft at the correct course and speed to intercept enemy aircraft using voice commands via ground-to-air radio. Initial equipment included the FPS-3 search radar and an MPS-14 height-finder radar. SAGE System TransitionThe transition of the manual GCI system to the automated SAGE system began with the installation of the FST-2 coordinate data transmitter and search radar upgrades. The FST-2 equipment digitized the radar returns and transmitted the digital returns to the SAGE direction center. Under the SAGE System, interceptor aircraft were directed to their targets by the direction center computers and controllers, greatly reducing the need for local controllers and equipment at every radar station. The FST-2 was a very large digital system using vacuum tube technology. Over 6900 vacuum tubes were used in each FST-2 requiring 21 air-conditioned cabinets, 40 tons of air conditioning, 43.5 kva of prime power, and usually a large new addition to the operations building. The FST-2B modification added two more cabinets but with newer solid-state (transistor) technology to process coded responses from aircraft transponders. SAGE System Operation
The site began operation as a SAGE site on 1 Nov 1959 initially feeding the Norton SAGE Direction Center DC-17 in San Bernardino, California. The search radar was upgraded to an FPS-20 in 1958 and an FPS-26A height-finder radar was installed in 1963. In 1961 Las Vegas AFS was an ADC/FAA joint-use facility and provided data for the FAA and the SAGE system. The FAA and USAF controllers both worked at the site operations building. The FPS-20 search radar was replaced with an FPS-27 search radar in the mid-1960s. The FAA retained the FPS-20A for their use. Control was transferred on 1 May 1961 to the Luke SAGE Direction Center DC-21 in Phoenix, Arizona Gap Fillers
Las Vegas AFS was responsible for maintaining two remote unattended gap-filler radar sites. The gap-filler sites were placed in locations where the main search radar lacked coverage. These sites sent digitized radar target data directly to a direction center. Maintenance teams were dispatched from Las Vegas AFS for regularly scheduled maintenance or when fault indicators suggested the site had problems. The two gap fillers built were at Boulder City, Nevada, and Lathrop Wells, Nevada. Two others were planned but not built. Air Force Station ClosureAbandoned by the Air Force in 1969 now Angel Peak FAA Radar Site. Angel Peak FAA Radar SiteWith the closure of the Air Force Station, the FAA assumed operation of the upper site with the FPS-20A search radar and provided data for the FAA ARTCCs and the SAGE system. A FYQ-47 Common Digitizer was probably placed in service by February 1973 when the USAF/FAA FST-2 to FYQ-47 replacement program was completed. By 1990 the site was equipped with an FPS-20A search radar and a CD-2A Common Digitizer. The Angel Peak CD-2A was scheduled to receive an upgrade kit to implement three-level weather data processing in June 1992. Mode S Beacon System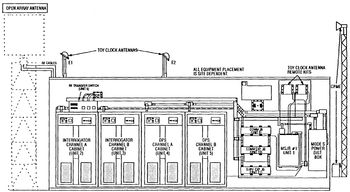 The Angel Peak FAA Radar Site was selected in the 1990s to become one of 21 long-range radar sites to have a Mode S radar beacon system installed. The Mode S system allowed operation in the existing beacon modes but added features to improve beacon operation by allowing aircraft identification with a single interrogation and two-way digital communication between controllers and pilots. Besides the 21 long-range sites, there were other short-range radars to be upgraded for a total of 137 sites on the implementation list. Angel Peak was #99 on the list, scheduled to receive the Mode S equipment on 30 Oct 1994. Installation required interfacing with the radar system, addition of a beacon antenna on top of the search radar antenna, a new larger radome, interfacing with the Common Digitizer (CD-2) if installed, additional communication lines and equipment. CARSR RadarThe nationwide replacement program converting FAA legacy radar systems to the CARSR radar configuration was completed by 17 Aug 2015 and Angel Peak FAA Radar Site was a part of that program. Legacy FAA radars underwent a Service Life Extension Program (SLEP) that replaced key components in the vintage ARSR-1, ARSR-2, FPS-20, FPS-66 and FPS-67 radars. The CARSR program replaced legacy klystron radar transmitters with a solid-state transmitter as well as renovating the radar receiver and signal processor. The CARSR modification also included common digitizer functionality making a separate common digitizer unnecessary. The Angel Peak FAA Radar Site is now operating with the CARSR radar. At the time of the CARSR changeout, the legacy radar in place was still the FPS-20A and the CARSR conversion included a 1561 Antenna. The secondary radar for the site is the Mode S Beacon set. The radar site data is now available to the USAF/NORAD Battle Control System-Fixed (BCS-F) operations centers (EADS & WADS) as well as the FAA Los Angeles ARTCC (ZLA) and adjacent ARTCCs. Other federal agencies have access to the data under the Homeland Security umbrella. Physical PlantThe physical plant of the site was divided into the main site, a cantonment area, and a radio site. The main site housed the operations buildings, the radar towers, and the backup generators. The Cantonment area housed the enlisted barracks, the bachelor officer's quarters, the orderly room, the dining hall, the motor pool, and other support buildings. Family housing was at Nellis Air Force Base. A separate Ground to Air Transmitter/Receiver (GATR) radio site housed the radio equipment for directing aircraft intercepts.
Current StatusAngel Peak FAA Radar Site on Angel Peak near Las Vegas, Clark County, Nevada. Lower Site is now the Spring Mountain Youth Camp. The upper site housed an FAA FPS-20A radar until the radar was upgraded to a Common Air Route Surveillance Radar (CARSR) in November 2014.
See Also:
Sources:
Fortification ID:
Visited: 11 Feb 2015
|


