Fort San Jacinto WWII Radar Site (2)
|
Fort San Jacinto WWII Radar Site (2) (1944-1946) - A World War II U.S. Army Radar Site established in 1944. Used to provide fire control information to large caliber (6" and above) coastal gun batteries in the Harbor Defense of the Galveston against enemy warships. Located on Fort San Jacinto near Galveston, Galveston County, Texas. Closed in 1946.
HistoryPart of the Harbor Defense of Galveston.
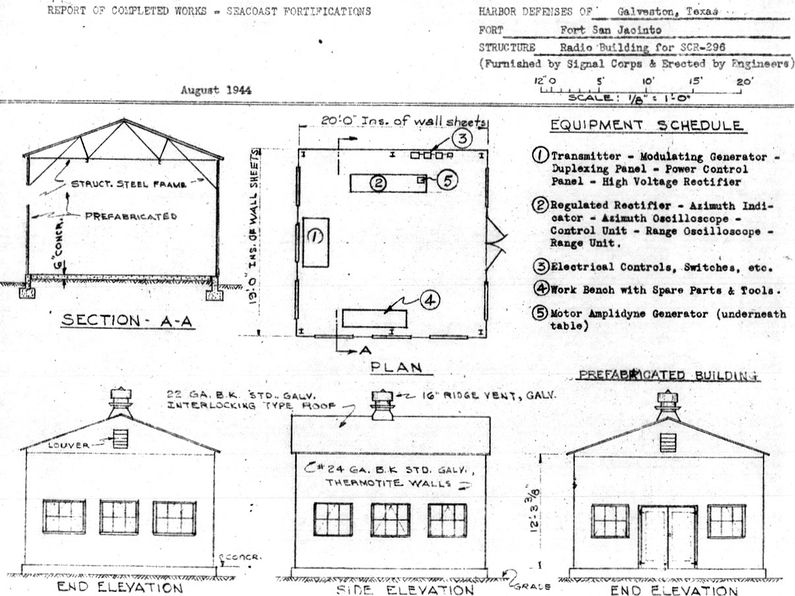
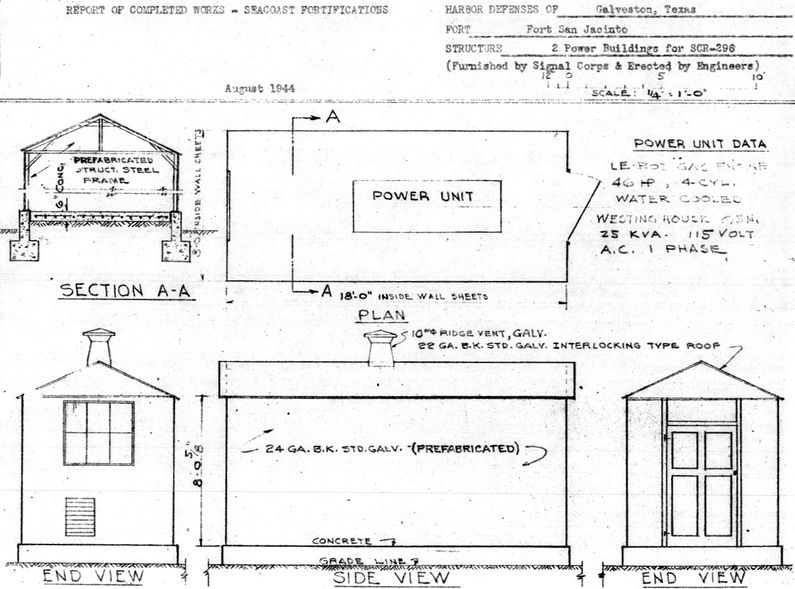
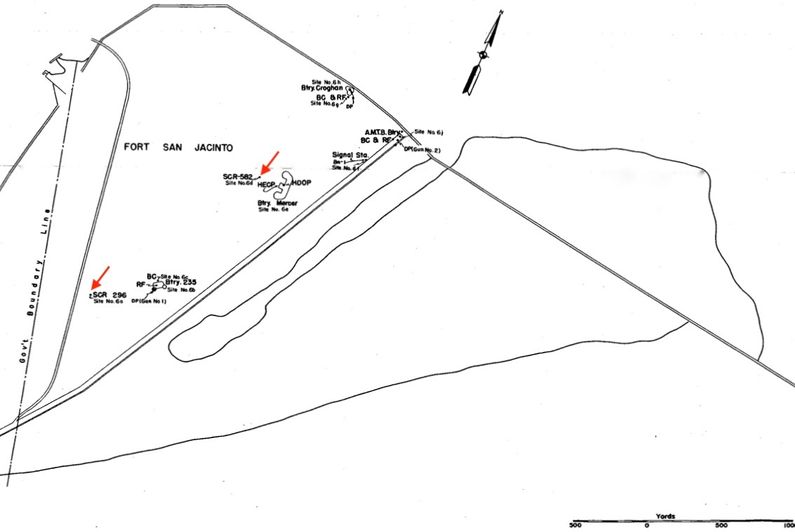
 Constructed and transferred for use on 28 Jun 1943 at Fort San Jacinto. Construction costs to date of transfer were $25,937.39. The physical plant consisted of a transmitter building, two powerhouses each with a 1000 gallon fuel tank, a 100' steel tower and an antenna housing disguised as a Water tank atop the tower. The three buildings and the tower were prefabricated steel units furnished by the Signal Corps. The buildings and the tower were placed on concrete pads and footings installed by the Corps of Engineers who erected all of the structures. Access to the antenna on top of the tower was by a small hoist operated by an electric motor.
Site Operation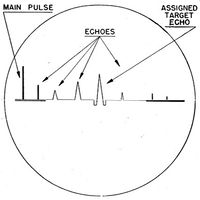 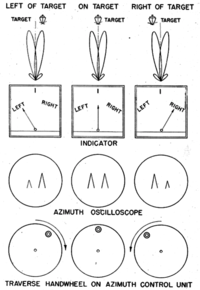 In operation, the SCR-296-A radar could only track one target at a time. Target assignments were made from the harbor HECP/HDCP command posts by telephone, citing the approximate range and azimuth of the target using the SCR-582/SCR-682 search radar and/or optical spotters. The SCR-296-A radar operators would then find the target and pass the precise range and azimuth to the plotting room at the gun battery by phone. Two operators were required, one for the range position and one for the azimuth position. The radar operators would continue to track the target and update the plotting room as the range and azimuth changed. Once the shore battery fired, the SCR-296-A could detect the water splashes of near misses and provide adjusting information by voice commands such as "300 short" or "500 long". 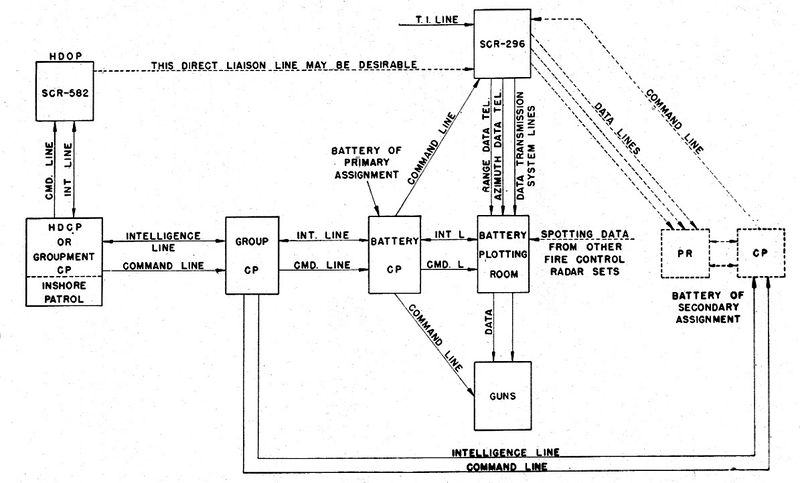 In operation, the range accuracy was about ± 30 yards while azimuth accuracy was about ± 0.20 degree under the best conditions. The set had a dependable range of 20,000 yards on a destroyer size target when properly sited between 150 to 500 feet above sea level. The operating crew consisted of 5 men plus a power plant operator and radar maintenance man. The Radar track data was provided by telephone to support Battery 235 as the primary battery and to secondary batteries including Battery Hoskins and Battery 234. Battery 235 was a 6" gun battery located on Fort San Jacinto. The SCR-296A Radar equipment was declared obsolete by AG letter on 17 Jan 1946. The Tower and radar equipment were to be disposed of while the buildings were to be retained.
ClosureClosed circa 1946. Current StatusNo visible remains.
See Also: Sources:
Links: Visited: No
| ||||||