Selfridge Air Force Base Radar Site
|
Selfridge Air Force Base Radar Site (1952-1974) - A Cold War Air Force Radar Station first established in 1952 on Selfridge Air Force Base, Macomb County, Michigan. Initially assigned a Permanent ID of P-20, later a Sage ID of Z-20. Abandoned in 1974. HistoryFirst established as a Lashup System Radar Site L-17 in 1949 with a CPS-5 search radar. Joined the permanent radar network in 1952 as site LP-20 and became operational using a pair of CPS-6 radar sets manned by the 661st AC&W Squadron. The station initially had both a Ground-Control Intercept (GCI) and early warning mission. The early warning mission involved tracking and identifying all aircraft entering their airspace while the GCI mission involved guiding Air Force interceptors to any identified enemy aircraft. Controllers at the station vectored fighter aircraft at the correct course and speed to intercept enemy aircraft using voice commands via ground-to-air radio. SAGE System TransitionThe transition of the manual GCI system to the automated SAGE system began with the installation of the FST-2 coordinate data transmitter and search radar upgrades. The FST-2 equipment digitized the radar returns and transmitted the digital returns to the SAGE direction center. Under the SAGE System, interceptor aircraft were directed to their targets by the direction center computers and controllers, greatly reducing the need for local controllers and equipment at every radar station. The FST-2 was a very large digital system using vacuum tube technology. Over 6900 vacuum tubes were used in each FST-2 requiring 21 air-conditioned cabinets, 40 tons of air conditioning, 43.5 kva of prime power, and usually a large new addition to the operations building. The FST-2B modification added two more cabinets but with newer solid-state (transistor) technology to process coded responses from aircraft transponders. SAGE System OperationThe site began operation as a SAGE site on 1 Oct 1959 initially feeding the Custer SAGE Direction Center DC-06. The search radar was upgraded to an FPS-20 and then to FPS-35 in 1961. One FPS-6 height-finder was removed and the other was replaced with a FPS-26A height-finder radar. In 1969 the Custer SAGE Direction Center DC-06 closed and the Selfridge SAGE site was switched to the Duluth SAGE Direction Center DC-10 until the site closed in 1974. NIKE SystemIn 1954 a U.S. Army NIKE System AADCP command post, D-15DC Selfridge Air Force Base, collocated with the radar site and shared the search radar data. A pre SAGE installation of Air Force GPA-37 equipment was slated to start in May 1959 to provide interim integration with the Army Missile Master system. The collocated NIKE command post upgraded with a Missile Master Blockhouse and an FSG-1 (Missile Master) acquisition, launch and guidance systems, later upgraded to an FSQ-51 (Missile Mentor) system. The U.S. Army also continued to share search radar data and added two FPS-6 height-finders in addition to the two USAF height-finders. ClosureThe Army deactivated the NIKE command post in June 1974. The Radar Site and the 661st were deactivated on 1 Jul 1974. Gap Filler Radar SitesSelfridge AFB Radar Site was responsible for the maintenance of four remote unattended gap-filler radar sites. The gap-filler sites were placed in locations where the main search radar lacked coverage. These sites sent digitized radar target data directly to a direction center. Maintenance teams were dispatched from Selfridge Air Force Base Radar Site AFS for regularly scheduled maintenance or when fault indicators suggested the site had problems. The Selfridge AFB Radar Site gap-filler radars were located at Burnside, MI; Emery MI; Marblehead, OH and Midland, MI.
Physical PlantThe physical plant of the site was divided into the main site, a cantonment area and a radio site. The main site housed the operations buildings, the radar towers, and the backup generators. The cantonment area housed the enlisted barracks, the bachelor officer's quarters, the orderly room, the dining hall, the motor pool and other support buildings. A separate Ground to Air Transmitter/Receiver (GATR) radio site housed the radio equipment for directing aircraft intercepts. Before the GATR radio site was built there were separate radio transmitter and receiver sites to the north and south of the main site. 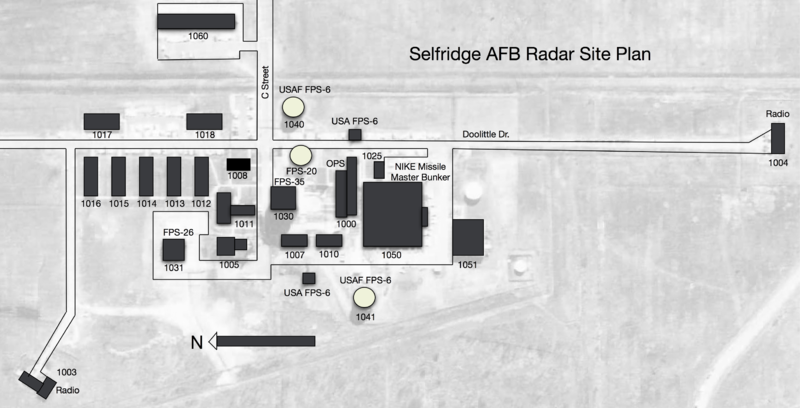
Current StatusThe Missile Master building was destroyed in 2005. The site is now the Selfridge Air Museum, some original buildings remain. The FPS-35 tower remains.
See Also:
Sources:
Links:
Visited: No
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||


