Larson Air Force Base
|
World War IIMoses Lake Army Air Base was activated on 24 Nov 1942 as a temporary World War II aircrew training center. Initially, it trained pilots for P-38s and later combat crews for B-17 Flying Fortresses. The base was established just north of the tri-cities of Pasco, Kennewick, and Richland, where the secret Hanford atomic bomb development took place, and close to the Bonneville and Grand Coulee hydroelectric dams on the Columbia River. The Bonneville dam opened in 1937 and the Grand Coulee dam opened in 1942 both became critical to the war effort, providing power not only for the Atomic bomb development but for aluminum production, and numerous defense plants and it provided water for crops irrigation. Post World War IIAt the end of the war in 1945, the military portion of the base was put on standby status, and Boeing Aircraft Company facilities associated with the base were used in the development and testing of the B-47 and the B-50 bombers. In 1947 the Air Force became a separate service and the Moses Lake Air Force Base was reactivated in November 1948 under the Air Defense Command. The mission of F-82, F-94, and F-86 fighters was to protect the vital Hanford Atomic Works, Bonneville & Grand Coulee Dams, and the coastal area. On 1 Apr 1952, Larson AFB was placed under the Tactical Air Command and the 62d Troop Carrier Wing moved from McChord AFB, Washington to assume command. During the next eight years, the 62d was prominent in national news events with missions in DEW Line and communications network construction, mercy flights, and flights to Formosa and Africa. 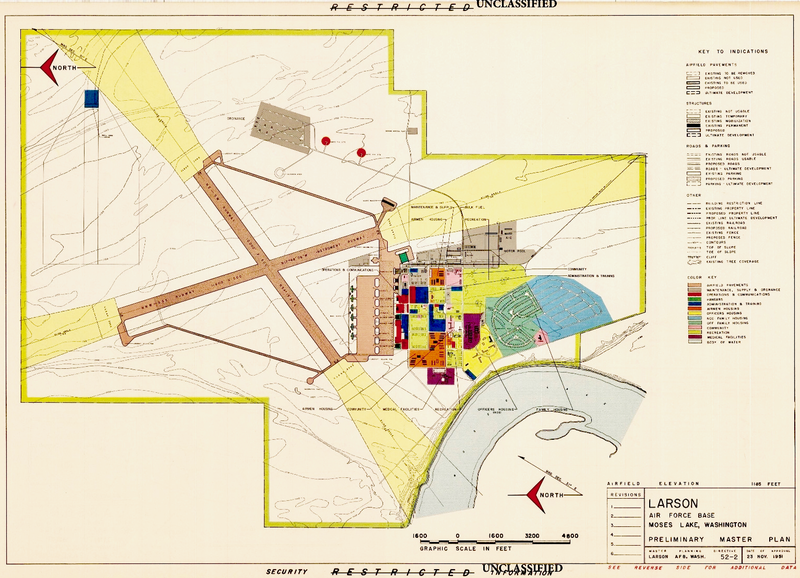 Larson became a Military Air Transport Service (MATS) base on 1 Jul 1957 and in June 1958 Larson was put under the newly created Western Transport Air Force of MATS. The Air Materiel Command (AMC) Flight Test Center at Larson tested B-52s at the field from February 1955 to 1959. Boeing built a $5.8 million hangar to accommodate eight B-52s or KC-135 tankers. The hangar was 1,068 feet long and 372 feet wide, with clear spans of 217 feet. The Strategic Air Command (SAC) assumed command of Larson AFB on 1 Jan 1960 and established the 462d Strategic Aerospace Wing as a part of its Fifteenth Air Force. The 568th Strategic Missile Squadron was officially activated on 1 April 1961 as a 4170th Strategic Wing unit. There were three Titan I missile complexes with three missile silos at each complex. The nine Titan I silos were evenly split between three sites near Odessa, Warden, and Othello, Washington. Support facilities were located at Larson AFB. The contractor(s) broke ground on 1 Dec 1959. The missile complexes were officially deactivated on 25 Mar 1965 and the missile sites were turned over to the General Services Administration (GSA) for disposal.
 The air defense mission continued at Larson AFB with the construction of the massive Larson SAGE Direction Center DC-15 in 1959 and the expansion of the nearby Othello Air Force Station. The Larson SAGE direction center was one of the first SAGE direction centers to close with most of its responsibilities assumed by the McChord SAGE Direction Center DC-12 on 1 Sep 1963. Othello Air Force Station continued to operate until 1975 when it closed.
ClosureOn 19 Nov 1965, the Secretary of Defense announced that Larson AFB was to be closed by June 1966. The Base was inactivated as an Air Force Installation effective 25 Jun 1966 as recorded by SO GA-60, DAF, Wash DC, 16 Aug 1966, para 4. Current StatusThe Air Force base closed in 1966 and the property is now the Grant County International Airport and has become a heavy jet training and testing facility used by the Boeing Company, Japan Airlines, the U.S. Military, and many other air carriers from around the world. With 4,700 acres and the main runway 13,500 feet long, it is one of the largest airports in the United States.
See Also: Sources:
Links:
Fortification ID:
Visited: 21 Aug 2014
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||