Eglin Air Force Base
|
Pre World War II(Text adapted from USAF Fact Sheet/History) In 1931, the Army Air Corps Tactical School at Maxwell Field, Alabama looking for a site for a bombing and gunnery range, they identified the sparsely populated forested areas surrounding Valparaiso, Florida, and the adjacent Gulf of Mexico as a suitable location. A local businessman and airplane buff, James E. Plew, leased to the City of Valparaiso 137 acres on which an airport was established in 1933. In 1934, Plew offered the U.S. government a donation of 1,460 contiguous acres for the bombing and gunnery base. This became the headquarters for the Valparaiso Bombing and Gunnery Base activated on 14 Jun 1935. World War IIWith the outbreak of WWII in 1939 General Henry H. "Hap" Arnold ordered the establishment of a proving ground for aircraft armament. Eglin was selected and on 27 Jun 1940, the U.S. Forestry Service ceded to the War Department the Choctawhatchee National Forest, consisting of some 384,000 acres. In 1941, the Air Corps Proving Ground was activated, and Eglin became the site for gunnery training for Army Air Forces fighter pilots, as well as a major testing center for aircraft, equipment, and tactics. To support these effort ten Auxiliary airfields were established within the reservation along with Eglin Field. In addition to testing all new aircraft and their modifications, the Proving Ground Command, established at Eglin in April 1942, found the isolation and immensity of the ranges especially well-suited for special tasks. In 1944, personnel developed the tactics and techniques to destroy German missile installations supporting the V-1 buzz-bomb attacks on England. Post WWII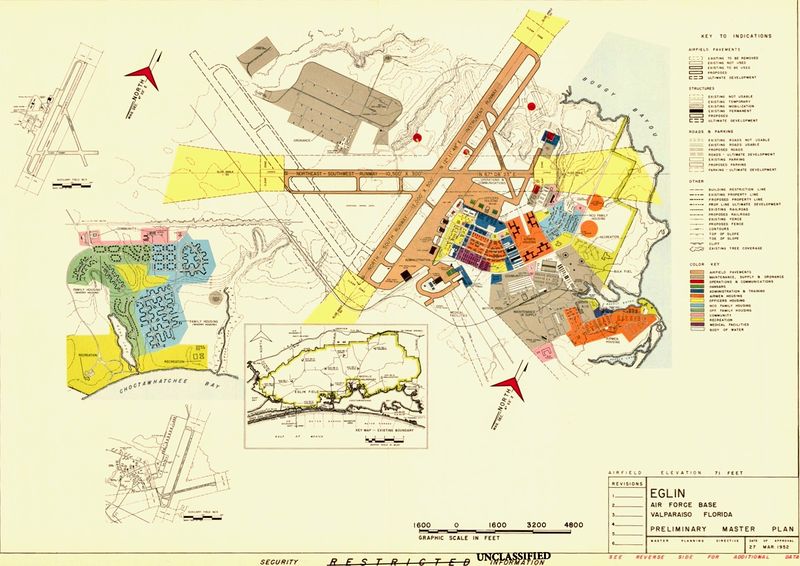 Eglin also became a pioneer in missile development and, in early 1946, the First Experimental Guided Missiles Group was activated to develop the techniques for missile launching and handling; establish training programs; and monitor the development of a drone or pilotless aircraft capability to support the Atomic Energy Commission tests, Operation CROSSROADS, at Eniwetok. On 13 Jan 1947. Cold WarIn reaction to the Soviet atomic bomb detonation in 1949 the Air Force, in early 1950, established the Air Research and Development Command (later Air Force Systems Command). After the start of the Korean War in 1950, test teams moved to the combat theater for testing in actual combat. They numbered among their accomplishments improved air-to-air tactics and improved techniques for close air support. On 1 Dec 1957, the Air Force combined the Air Proving Ground Command and the Air Force Armament Center to form the Air Proving Ground Center. The Air Proving Ground Center built the highly-instrumented Eglin Gulf Test Range and for the next few years, served as a major missile test center for weapons such as the BOMARC, Matador, GAM-72 "Quail," and GAM-77 "Hound Dog." As the Southeast Asia conflict increased emphasis on conventional weapons, the responsibilities at Eglin grew. On 1 Aug 1968, the Air Proving Ground Center was redesignated the Armament Development and Test Center to centralize responsibility for research, development, test and evaluation, and initial acquisition of nonnuclear munitions for the Air Force. In 1975, the installation served as one of four main U.S. Vietnamese Refugee Processing Centers, where base personnel housed and processed more than 10,000 Southeast Asian refugees at the Auxiliary Field Two "Tent City." Eglin again became an Air Force refugee resettlement center processing over 10,000 Cubans who fled to the U.S. between April and May of 1980. On 11 Jul 1990, the Munitions Systems Division was redesignated the Air Force Development Test Center. During the 1990s, the Center supported test and evaluation for the development of nonnuclear Air Force armament including next generation precision-guided weapons; operational training for armament systems; and test and evaluation of command, control, communications, computers, and intelligence aerospace navigation and guidance systems. Post Cold WarOn 1 Oct 1998, the Air Force Development Test Center became the Air Force Materiel Command's Air Armament Center (AAC). As one of AFMC's product centers, AAC is responsible for development, acquisition, testing, and fielding all air-delivered weapons. On 18 Jul 2012, the Air Armament Center was deactivated as part of a consolidation effort to reduce Air Force Materiel Command's number of centers from 12 to five. On the same day, the 46th Test Wing and 96th Air Base Wing were merged to create the 96th Test Wing. The 96 TW houses all of Eglin's test and support functions on the US Air Forces largest installation. In late 2018, following the destruction of Hurricane Michael, Eglin provided support for displaced Tyndall AFB personnel and logistics to assist in base recovery. Air Force leaders made the decision to temporarily relocate the F-22 Formal Training Unit of 325th Fighter Wing (ACC) to Eglin AFB, to include F-22 Raptor and T-38 Talon aircraft. 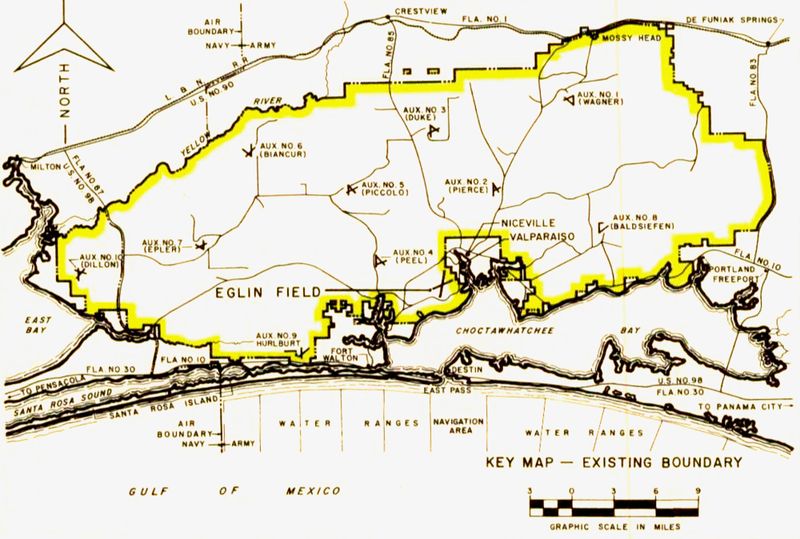
Current Status
See Also: Sources: Links: Fortification ID:
Visited: No
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
