Camp Ibis
|
Camp Ibis (1942-1944) - A World War II desert training camp established in 1942 near Needles in San Bernardino County, California. Camp Ibis was named after the Ibis Railyard. Abandoned in 1944.
History Established in 1942 as one of thirteen temporary World War II training camps in the southern California and Arizona desert areas. These training camps formed what was initially known as the Desert Training Center and then as the California-Arizona Maneuver Area after 20 Oct 1943. As the war entered a new phase in 1944, the camps were closed and training was discontinued on 30 Apr 1944. 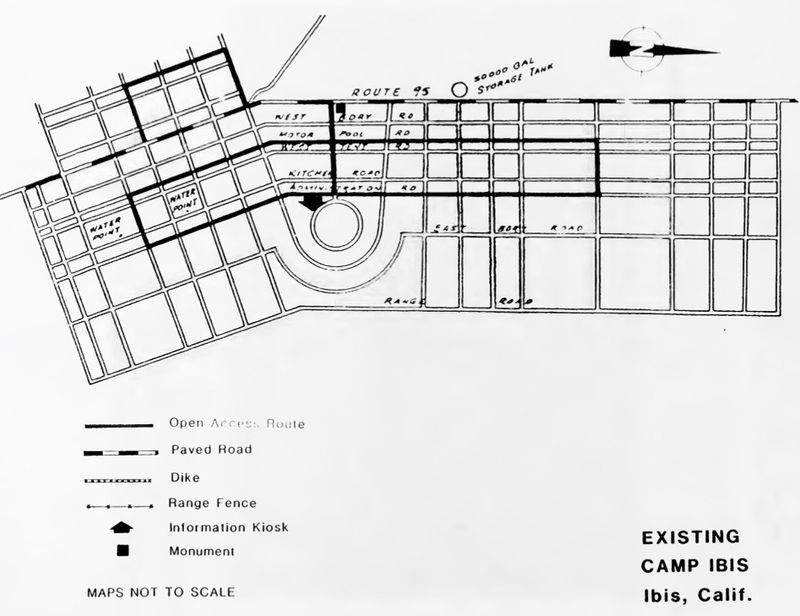
Temporary facilities constructed on the site include 28 enlisted men's shower buildings, 14 officer's shower buildings, 173 latrines, 234 various pyramided wood tent frames, and a 50,000-gallon wooden elevated storage tank. Water for the site was provided by deep well pumps. The only permanent structure constructed on the site was one 50,000-gallon concrete reservoir. At least 23 firing ranges were provided on the site. The ranges accommodated a variety of pistols, rifles, machine guns, and tank guns. Camp Ibis Army AirfieldThe U.S. Army built an airfield at Camp Ibis to support the training operations. The airfield had a single 4,500' north/south runway located on the west side and adjacent to what is now U.S. Hwy 95 about 13 miles northwest of Needles, California. ClosureCamp Ibis was declared surplus on 16 Mar 1944 and 5,760 acres were transferred from the War Department to the Department of the Interior. Leased land was returned to the various owners. Post WarRestricted use of the land continued after the war while the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) supervised the cleanup of the hazardous material and the removal of temporary facilities. A 1951 USACE & BLM letter recommended that 20,640 acres, including 3,840 acres of the Campsite be restricted to surface use only. Another 11,520 acres were certified clear. Current Status Surface remains only, the outline of the camp road structure and the airstrip can be seen from satellite views. A roadside marker has been placed on the east side of U.S. HWY 95 at the main entrance to the camp. The kiosk indicated in the Draft Interpretive Plan below is not at the location indicated. The central road to the camp center circle (M to C on the map below) is drivable by ordinary cars, some of the other roads may require high clearance vehicles.
See Also: Sources:
Links: Visited: 15, 23 Feb 2017
| ||||||
